Boilers are a cornerstone of home heating in the UK, providing warmth and hot water to millions of households. However, not all boilers are the same, and understanding the types available, as well as how they work, can help you make informed decisions when maintaining, upgrading, or choosing a new system.
1. The Main Types of Boilers in the UK
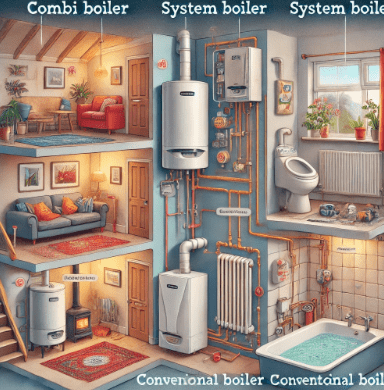
a. Combi Boilers (Combination Boilers)
Combi boilers are the most common type of boiler in UK homes. They combine heating and hot water in a single unit, eliminating the need for a separate water storage tank.
Key Features:
- Hot water is heated on demand directly from the mains.
- Space-saving as no additional cylinder or tank is required.
- Ideal for smaller homes with limited space.
Mechanism:
When you turn on a tap, the combi boiler heats water instantaneously using a heat exchanger. For heating, the system circulates hot water through radiators or underfloor heating pipes.
b. System Boilers
System boilers require a hot water storage cylinder but no cold water tank. They are well-suited for homes with higher hot water demands.
Key Features:
- Provides a steady supply of hot water to multiple taps at the same time.
- More compact than conventional boilers as they don’t require a cold water tank.
- Suitable for medium to large homes.
Mechanism:
System boilers heat water directly from the mains, storing it in the cylinder for later use. The stored water is then distributed for hot water taps or radiators when needed.
c. Conventional Boilers (Regular or Heat-Only Boilers)
Conventional boilers are the traditional systems often found in older homes. They require both a hot water cylinder and a cold water tank.
Key Features:
- Reliable for homes with high water usage.
- Ideal for properties with old radiator systems that might not be compatible with high-pressure systems.
- Require more space for tanks and cylinders.
Mechanism:
Cold water from the tank is heated in the boiler and stored in the hot water cylinder. The system then distributes hot water to taps or radiators as required.
d. Electric Boilers
Electric boilers are less common but are an option for homes without access to gas or oil.
Key Features:
- Eco-friendly and suitable for small properties.
- Higher running costs compared to gas boilers.
- Compact and easy to install.
Mechanism:
Electricity heats water using heating elements. The hot water is then circulated through the heating system or stored in a cylinder, depending on the boiler type.
2. How Boilers Heat Your Home
Boilers function by heating water and circulating it through a network of pipes to radiators, underfloor heating systems, or directly to taps. Here’s a closer look at the heating mechanism:
Step 1: Heat Generation
- Gas Boilers: Burn natural gas to create heat. A heat exchanger transfers the heat to water in the system.
- Electric Boilers: Use electricity to heat water directly.
- Oil Boilers: Burn oil instead of gas to generate heat.
Step 2: Water Circulation
- Heated water is pumped through a system of pipes to radiators or underfloor heating systems, providing warmth throughout the home.
Step 3: Hot Water Supply
- For combi boilers, hot water is provided directly to taps and showers on demand.
- For system and conventional boilers, hot water is stored in a cylinder and distributed when needed.
Step 4: Return and Reheat
- The water cools down as it travels through the system and returns to the boiler to be reheated, completing the cycle.
3. Choosing the Right Boiler for Your Home
The best boiler for your home depends on factors like the size of your property, hot water usage, and available space.
- Smaller homes: Combi boilers are a great choice due to their compact design and on-demand heating.
- Larger homes or high water usage: System or conventional boilers are more suitable to handle simultaneous demands.
- Eco-conscious homes: Electric boilers or systems compatible with renewable energy sources may be preferable.
4. Maintenance Tips for Efficient Heating
- Annual Servicing: Have your boiler serviced annually by a Gas Safe registered engineer.
- Bleed Radiators: Remove trapped air to ensure efficient heating.
- Insulate Pipes: Prevent heat loss and protect pipes from freezing in winter.
- Use a Smart Thermostat: Optimize energy usage by controlling heating schedules remotely.
Understanding the types of boilers and their mechanisms can help you keep your home warm efficiently while saving on energy bills. Choose a system that suits your household needs and maintain it regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Our Whatsapp broadcast List (English): https://livinintheuk.com/broadcast_en