介紹:
日本虎杖(Fallopia japonica)是一種在英國引起重大關注的入侵植物物種。儘管它以竹子般的茎幹和寬闊的葉子具有美感,但日本虎杖以其破壞性的特性而聞名。它快速蔓延並侵蝕建築物的能力使其成為房主、企業和環境當局的強大對手。本文旨在介紹日本虎杖,並提供在英國如何有效處理和管理它的指導。
了解日本虎杖:
日本虎杖起源於東亞,於19世紀作為觀賞植物引入英國。然而,由於其頑強的特性,它很快在野外建立起來並在全國成為一個問題。該植物具有廣泛的根系,稱為根莖,可以長達三米深七米寬。這使得它能夠迅速蔓延,對基礎設施、生物多樣性造成損害,並降低財產價值。
法律影響:
日本虎杖存在於房產中可能具有法律影響。在英國,根據1990年的環境保護法案,該植物被歸類為“受控廢物”,並受到嚴格的法規限制。禁止允許該植物擴散到鄰近房產,或不當處置,例如將其倒入鄉村。不解決日本虎杖的入侵可能導致法律訴訟、罰款,以及出售或獲得受影響房產的抵押貸款困難。
有效管理策略:
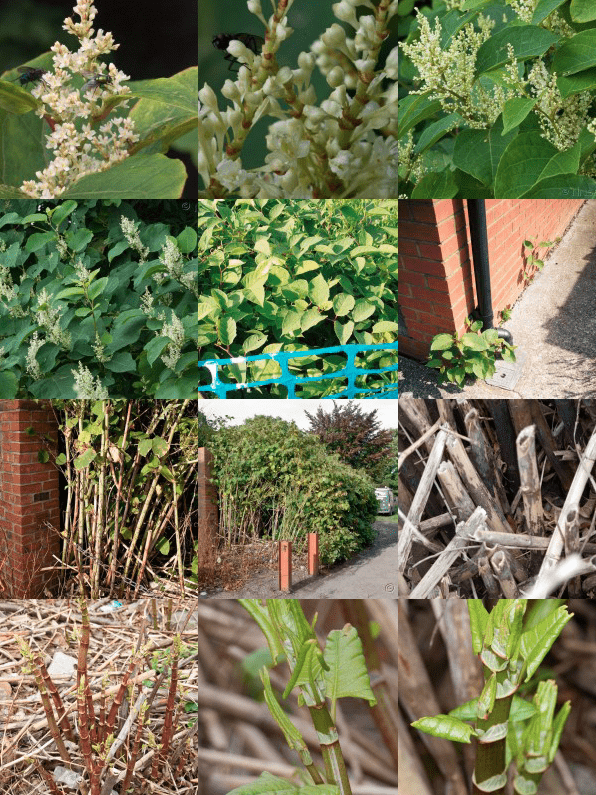
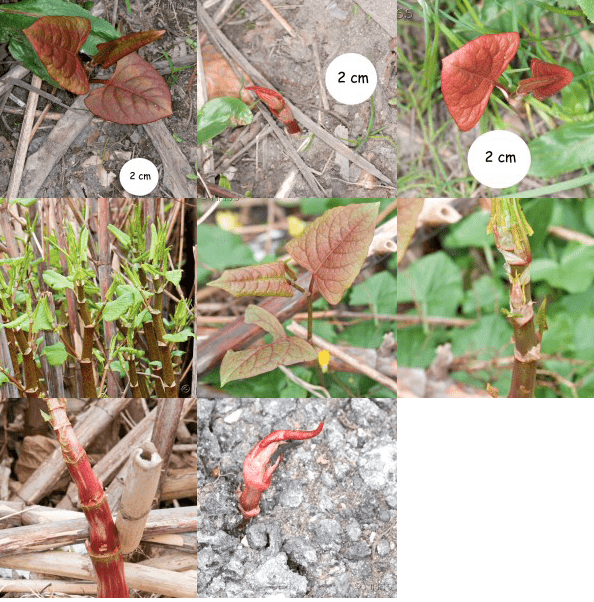
- 早期檢測:在日本虎杖的早期階段識別它是有效管理的關鍵。該植物通常在春季出現,具有快速生長的紅色或紫色芽,這些芽會迅速生長為高大、中空的茎幹。其獨特的盾狀葉片和白色花朵也是可識別的特徵。如果您懷疑房產上存在日本虎杖,請尋求專業建議以進行準確鑒定。
- 專業協助:處理日本虎杖需要專業知識和專業技術。建議與熟悉該植物識別和管理的合格專家合作。他們將評估入侵程度,提出適當的治療方案,並提供符合法規的必要文件。
- 治療方法:可以采用多種方法來控制日本虎杖,包括化學治療、挖掘和埋藏,以及使用專業薄膜抑制生長。化學治療,如除草劑,通常用於隨時間抑制植物生長。嚴重入侵情況可能需要進行挖掘並在經過許可的垃圾填埋場處置。
- 長期監測:日本虎杖具有持久性,定期監測對確保其根除至關重要。即使在初步治療後,保持警惕並及時處理任何再生情況也很重要。專業人士的跟進檢查將有助於識別和管理任何潛在再發情況。
- 法律義務:在處理日本虎杖時,遵守法律要求至關重要。與專業人士密切合作,以獲得有關所需文件(如管理計劃和廢物轉移記錄)的建議。這些文件將證明已經采取適當的步驟負責地管理該植物。
結論:
日本虎杖對英國的房產和環境構成了重大挑戰。然而,採取正確的方法並獲得專業協助,是有效管理和控制這種入侵植物的可能。早期檢測、尋求合格專家的協助、選擇適當的治療方法以及遵守法律義務是對抗日本虎杖的關鍵步驟。通過采取積極的措施並及時獲取資訊,我們可以保護自己的財產並保護周圍環境的生物多樣性。
Tackling Japanese Knotweed: A Guide to Managing the Invasive Plant in the UK
Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica) is an invasive plant species that has been causing significant concerns in the United Kingdom. Despite its aesthetic appeal with its bamboo-like stems and broad leaves, Japanese Knotweed has earned a notorious reputation for its destructive nature. Its ability to spread rapidly and penetrate structures has made it a formidable adversary for homeowners, businesses, and environmental authorities. This article aims to shed light on Japanese Knotweed and provide guidance on how to effectively handle and manage it in the UK.
Understanding Japanese Knotweed:
Originating from Eastern Asia, Japanese Knotweed was introduced to the UK as an ornamental plant in the 19th century. However, due to its resilient nature, it quickly established itself in the wild and became a problem across the country. The plant has an extensive root system, known as rhizomes, which can grow up to three meters deep and seven meters horizontally. This allows it to spread rapidly, causing damage to infrastructure, biodiversity, and reducing property values.
Legal Implications:
The presence of Japanese Knotweed on a property can have legal implications. In the UK, the plant is classified as “controlled waste” under the Environmental Protection Act 1990 and is subject to strict regulations. It is illegal to allow the plant to spread to neighboring properties or to dispose of it inappropriately, such as dumping it in the countryside. Failure to address Japanese Knotweed infestations can result in legal action, fines, and difficulties in selling or obtaining a mortgage for affected properties.
Effective Management Strategies:
- Early Detection: Identifying Japanese Knotweed in its early stages is crucial for effective management. The plant typically emerges in spring, with red or purple shoots that grow rapidly into tall, hollow stems. Its distinctive shield-shaped leaves and white flowers are also identifiable characteristics. If you suspect the presence of Japanese Knotweed on your property, seek professional advice for accurate identification.
- Professional Assistance: Dealing with Japanese Knotweed requires expertise and knowledge. Engaging a qualified specialist who has experience in its identification and management is highly recommended. They will assess the extent of the infestation, propose appropriate treatment options, and provide necessary documentation for legal compliance.
- Treatment Options: Several methods can be employed to control Japanese Knotweed, including chemical treatment, excavation, and burial, and the use of specialized membranes to inhibit growth. Chemical treatments, such as herbicides, are often used to suppress the plant’s growth over time. Excavation and disposal at licensed landfill sites may be necessary for severe infestations.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Japanese Knotweed is persistent, and regular monitoring is essential to ensure its eradication. Even after initial treatment, it is important to remain vigilant and address any regrowth promptly. Follow-up inspections by professionals will help identify and manage any potential reoccurrences.
- Legal Obligations: When dealing with Japanese Knotweed, it is crucial to comply with legal requirements. Work closely with professionals who can advise on the necessary documentation, such as a management plan and waste transfer notes. These documents will demonstrate that appropriate steps have been taken to manage the plant responsibly.
Conclusion:
Japanese Knotweed poses a significant challenge for property owners and the environment in the UK. However, with the right approach and professional assistance, it is possible to manage and control this invasive plant effectively. Early detection, engaging qualified specialists, selecting appropriate treatment methods, and adhering to legal obligations are key steps in combating Japanese Knotweed. By taking proactive measures and staying informed, we can protect our properties and preserve the biodiversity of our surroundings.





